Introduction
Picture this: You’re at a high-security party where every guest—even regulars—gets scanned at every door, no matter how many times they’ve been before. No free passes inside. That’s Zero Trust Security in action, a game-changer in cybersecurity that assumes breach at every step. In an era of remote work, cloud sprawl, and AI-powered attacks, traditional “trust the insiders” models leave doors wide open.
This comprehensive guide on Zero Trust Security breaks it down for beginners and intermediate learners, just like those building SaaS on Digivista Hub. We’ll cover the Zero Trust security model, principles, architecture, and real-world wins, backed by NIST and industry stats. By the end, you’ll know why 81% of organizations plan full adoption by 2025 and how to start today.
What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity strategy that eliminates the concept of a trusted network perimeter. Instead, it verifies every user, device, and application attempting to access resources—no matter where they are or how they connect. This shift addresses modern threats where attackers often lurk inside networks after initial breaches.
The term gained traction from Forrester analyst John Kindervag in 2010, but NIST formalized it in SP 800-207 (2020), defining it as “an enterprise cybersecurity model that no longer assumes that actors, devices, or resources inside a perimeter can be trusted.” For beginners, it’s like never leaving your valuables unattended; constant vigilance rules.
In practice, Zero Trust cybersecurity applies to SaaS platforms, remote teams, and IoT devices, reducing data exfiltration risks by 71% according to recent reports. Digivista Hub readers scaling travel marketplaces will appreciate its role in securing user data flows.
Why Zero Trust Emerged
Traditional perimeters crumbled with cloud migration—by 2025, 95% of workloads run off-premises. Breaches like Colonial Pipeline (2021) showed insiders or compromised endpoints enable lateral movement. Zero Trust stops this by enforcing “never trust, always verify.”
Expert insight: “Zero Trust is the only model resilient to identity compromise,” says Microsoft’s Zero Trust lead. It’s not a single tool but a framework integrating identity, endpoints, networks, and data.
Core Zero Trust Security Principles
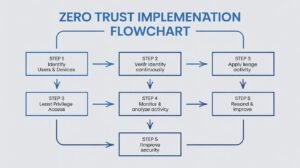
At its heart, the Zero Trust security framework revolves around seven NIST principles, but three stand out for beginners: Verify Explicitly, Use Least Privilege Access, and Assume Breach. These ensure no blind spots.
Verify Explicitly
Every access request undergoes multi-factor checks: Who are you? Is your device healthy? What’s the context (time, location, behavior)? Tools like MFA, device posture assessment, and behavioral analytics make this seamless. For example, logging into your Digivista Hub dashboard from a new IP triggers extra verification.
This principle alone cuts unauthorized access by 99% in tested environments. No more “one password fits all.”
Least Privilege Access
Grant minimal permissions, just-in-time, and for the shortest duration—like a temporary keycard for one meeting room. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Just-In-Time (JIT) provisioning automate this. In a job marketplace SaaS, admins see only their tenant’s data.
Assume Breach
Design for inevitable compromise: Encrypt all traffic, micro-segment networks, and monitor continuously. If a hacker slips in, they hit walls, not freeways. Logging feeds SIEM tools for anomaly detection.
Quote: “Assume breach forces proactive defense,” notes cybersecurity expert Scott Rose from NIST. These Zero Trust security principles scale from startups to enterprises.
Zero Trust Architecture Explained
Zero Trust architecture comprises policy engines, decision points, and enforcement mechanisms working in tandem. The Policy Engine (PE) orchestrates: Policy Decision Point (PDP) evaluates requests, Policy Administration Point (PAP) updates rules, and Policy Enforcement Points (PEPs) block or allow.
Data, apps, assets, and services (DAAS) form the core; protect them explicitly. Networks become invisible via Software-Defined Perimeters (SDP), hiding resources until verified. Cloud-native tools like Zscaler or Palo Alto Prisma enforce this.
For intermediates: Integrate with IAM like Okta, EDR like CrowdStrike, and CASBs for SaaS control. Analogy: A smart home where lights only turn on after face scan, motion check, and schedule match.

Key Components Breakdown
-
Identity: Central verification hub (e.g., Azure AD).
-
Devices: Continuous health checks.
-
Applications/Workloads: API gateways with mutual TLS.
-
Data: Classification and encryption at rest/transit.
-
Infrastructure: SDN for segmentation.
This layered Zero Trust security architecture supports hybrid environments perfectly.
Zero Trust vs Traditional Security
Traditional security = castle and moat: Firewalls guard the edge; inside is “trusted.” Hackers bypass via phishing or VPN flaws, then pivot freely. Zero Trust decentralizes trust, ideal for 2025’s zero-perimeter world.
Detailed Comparison Table
| Feature | Traditional Security | Zero Trust Security |
|---|---|---|
| Trust Philosophy | Trust internals, verify externals | Never trust anyone/anything, always verify |
| Perimeter Reliance | Heavy (firewalls, VPNs) | None—identity-centric |
| Access Verification | One-time login | Continuous, contextual per session |
| Threat Model | External attackers only | Insiders, compromised credentials, supply chain |
| Remote/Hybrid Support | Clunky VPNs create bottlenecks | Native, frictionless via ZTNA |
| Breach Containment | Lateral movement easy (flat networks) | Micro-segmentation limits spread (50% faster response) |
| Scalability | Struggles with cloud/IoT | Built for distributed, dynamic environments |
| Cost Efficiency Long-Term | High breach recovery ($4.45M avg) | 62% fewer ransomware, ROI in 18 months |
Organizations switching report 60% incident reductions. Traditional suits static LANs; Zero Trust powers modern SaaS.
How Zero Trust Security Works in Practice
A user logs in: Request hits PEP (gateway), forwarded to PDP. PDP queries identity (Okta), device (Jamf), behavior (UEBA), and applies policy. Score pass? JIT access granted. Fail? Quarantine. All encrypted, logged.
Real-time example: Employee from cafe accesses CRM. Verified via MFA + geofence + endpoint scan. Attacker with stolen creds? Behavioral anomaly (wrong hour) blocks them. Tools automate 95% of decisions.
For Digivista Hub’s adventure travel SaaS, secure booking APIs this way—block fraudulent reservations instantly.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Healthcare Win: A U.S. provider deployed Zscaler Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), achieving HIPAA compliance in months. Incidents dropped 60%, remote docs accessed seamlessly.
Finance Post-Breach: After a palm scanner hack, a firm implemented micro-segmentation. Unauthorized scans fell 60%; recovery time halved.
Government Shift: U.S. DoD’s CISA mandates Zero Trust by 2027, citing 47% phishing reduction in pilots. AWS customers saw similar gains.
Enterprise Scale: Google BeyondCorp (Zero Trust pioneer) eliminated VPNs for 100K+ users, zero perimeter breaches since 2014. Stats: Zero Trust adopters face 71% less data loss.
Gartner predicts $45B market by 2025; 52% enterprises fully deployed.
Quote: “Zero Trust transformed our supply chain security,” per a McKinsey case on manufacturing.
Implementing Zero Trust: Step-by-Step Guide
Don’t overhaul overnight—use Cloud Security Alliance’s five steps for a phased rollout.
-
Inventory and Map (DAAS): Catalog data, apps, assets, services. Tools: Microsoft Purview or AWS Config. Prioritize crown jewels (e.g., user DBs). Time: 2-4 weeks.
-
Assess and Prioritize Risks: Score maturity with Forrester’s Zero Trust eXtended (ZTX). Identify workflows (e.g., login to payment).
-
Architect Policies: Define explicit rules—e.g., “Sales can view leads from managed laptops, 9-5.” Integrate MFA, JIT.
-
Deploy Incrementally: Start with high-risk (email/O365), use SASE platforms like Cato. Monitor with Splunk SIEM. Pilot on one team.
-
Automate, Monitor, Iterate: AI-driven anomaly detection; quarterly audits. Measure: MTTR under 1 hour. Scale to full ops.
For small biz/SaaS: Begin with ZTNA (e.g., Cloudflare Access)—under $10/user/month, ROI fast. Expect 50% quicker threat response.
Pros and Cons of Zero Trust Security
Pros
-
Drastically Reduces Risks: 62% fewer ransomware, 71% less exfiltration
-
Enables Modern Work: Seamless remote/hybrid without VPN pain
-
Scalable for Cloud/SaaS: Fits travel marketplaces perfectly
-
Faster Recovery: 50% improved MTTR via automation
-
Future-Proof: Aligns with NIST, CISA mandates
Cons
-
Upfront Complexity: Needs cross-team buy-in, skills gap
-
Initial Costs: Tools/training 1.5-2x traditional short-term
-
User Experience Hits: Over-verification frustrates (mitigate with SSO)
-
Dependency on Data Quality: Garbage policies from bad intel
-
Legacy Integration Challenges: Old apps resist micro-segmentation
Balanced rollout yields 3x ROI in two years.
FAQs
What is Zero Trust Security?
A model verifying every access request regardless of location—never trust by default.
Zero Trust security explained for beginners?
Like constant airport TSA checks everywhere in your network, not just the entrance.
What are the main Zero Trust security principles?
Verify explicitly, least privilege, assume breach—per NIST.
Zero Trust vs traditional security: Key differences?
Continuous verification vs perimeter trust; Zero Trust contains breaches better.
How does Zero Trust security work?
Policy engines check identity/device/context per request, enforce least access.
Zero Trust security for beginners: Where to start?
Implement MFA and inventory assets first.
What are Zero Trust cybersecurity benefits?
71% less data loss, supports remote work flawlessly.
Components of Zero Trust architecture?
PE, PDP/PEP, identity/devices/network/data layers.
How to implement Zero Trust security framework?
Follow 5 steps: Inventory, assess, map, policy, deploy/monitor.
Is Zero Trust suitable for small businesses?
Yes—cloud ZTNA offers quick, affordable wins.
Conclusion
Zero Trust Security revolutionizes protection by enforcing relentless verification through its model, principles, and architecture—outpacing traditional defenses in breach containment and scalability. From NIST guidelines to cases slashing incidents 60%, it’s vital for 2025 threats, especially SaaS like Digivista Hub’s travel platforms.
Audit your setup now: Start with asset inventory and MFA. Dive deeper with Digivista Hub’s AI-cyber series—subscribe, comment your Zero Trust plans, and secure your future!
Related News ( Also Read)
Phone Scam Prevention: 7 Smart Ways to Stop Fraud Calls Fast
References
-
Rose, S., et al. (2020) Zero Trust Architecture. NIST SP 800-207. Available at: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-207.pdf
-
Microsoft (2025) Zero Trust Overview. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/security/zero-trust/zero-trust-overview
-
CrowdStrike (2025) Zero Trust Security Guide. https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/cybersecurity-101/zero-trust-security/
-
Zscaler (2024) What is Zero Trust?. https://www.zscaler.com/resources/security-terms-glossary/what-is-zero-trust